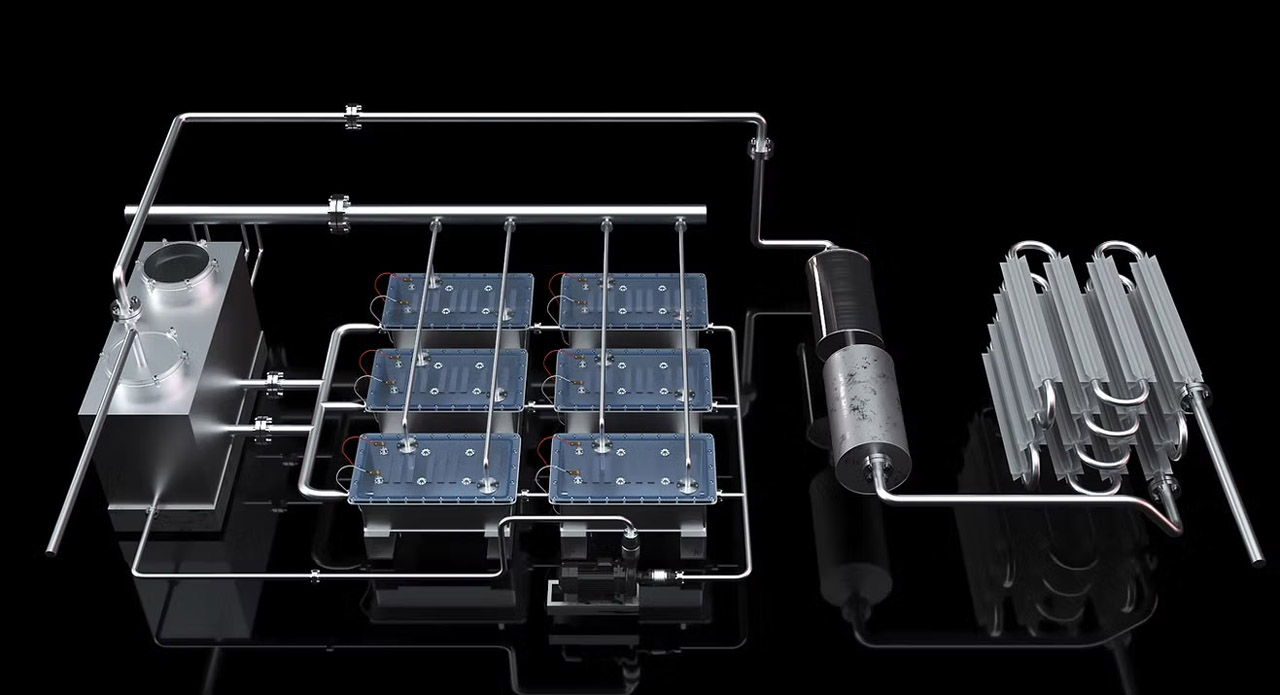
Advantages of SCL's E-beam Electrolysis
The
biggest and most remarkable advantage of SCL's technology is the low amount of
energy required for hydrogen production. The electrical energy needed is only
one-fifth compared to other electrolysis methods. It’s so astonishing that you
have to see it to believe it.
Another
advantage is that any type of water can be used. Since 10 liters of water are
needed for every kilogram of hydrogen, water consumption is high, and if the
water needs to be purified, it adds extra steps and costs.
An
additional benefit is that the process has no energy losses. Energy losses
typically produce heat that needs to be cooled. In this case, the water stays
around 40°C the entire time, and no cooling is required.
The World’s Cheapest Green Hydrogen
Several
companies are investing heavily in research to produce hydrogen with lower
energy losses. The large hydrogen projects being planned require vast amounts of electricity. This makes the projects expensive, and it may be difficult to supply all the electricity needed.
That the
technology from SCL and Professor Lee can produce 1 kg of hydrogen using only
10 kWh/kg sounds too good to be true. This opens
up completely new possibilities for achieving profitability and reduces
dependence on available green electricity.